Understanding Heat Shields

What Are Heat Shields On A Car ?
Heat shields play an essential yet often overlooked role in ensuring the smooth and safe operation of your vehicle. Beneath the sleek sheet metal that forms the car’s exterior lies a complex network of components that generate and endure significant amounts of heat. One of the most critical tasks of these components is to manage and mitigate the excessive heat produced by the engine and exhaust system. The engine and exhaust systems are the primary sources of heat in a car. The exhaust manifold and catalytic converter, for instance, operate at high temperatures due to the heat generated by the burning of fuel. Without proper management, this exhaust heat can damage vehicle components, reduce efficiency, and even pose a hazard to passengers. That’s where heat shields on cars come into play.
Constructed typically from stainless steel—a material prized for its durability and heat-resistant properties—heat shields protect sensitive parts of the vehicle from the extreme heat produced by the exhaust system. Stainless steel has a melting point of around 1,400 to 1,550 degrees Celsius (2,550 to 2,820 degrees Fahrenheit), making it an ideal thermal barrier to shield the rest of the car from the high temperatures of the exhaust manifold and catalytic converter. These thermal barriers effectively block the radiant heat from reaching other components and the car’s interior. By reflecting or dissipating the heat, they prevent damage to the vehicle’s parts and ensure passenger comfort. The technical parameters of these shields, such as their thermal conductivity (which for stainless steel is about 16.2 W/m-K at room temperature), give us an insight into how they manage heat transfer. This low thermal conductivity means that stainless steel does not easily allow the passage of heat, making it an excellent material for the job.
Moreover, the heat shields serve to protect the car from the exhaust heat’s potential to ignite flammable materials—like oil or grease—which might have accumulated under the vehicle. By keeping the exhaust system at a safe distance from these flammables, the shields add an extra layer of safety to the car’s operation. In summary, the heat shields in a car are unsung heroes, offering protection against the excessive heat produced by the engine and exhaust. They ensure that the car heat remains at manageable levels, safeguarding the vehicle’s performance and the safety of its occupants from the potential dangers of high temperatures and heat transfer.
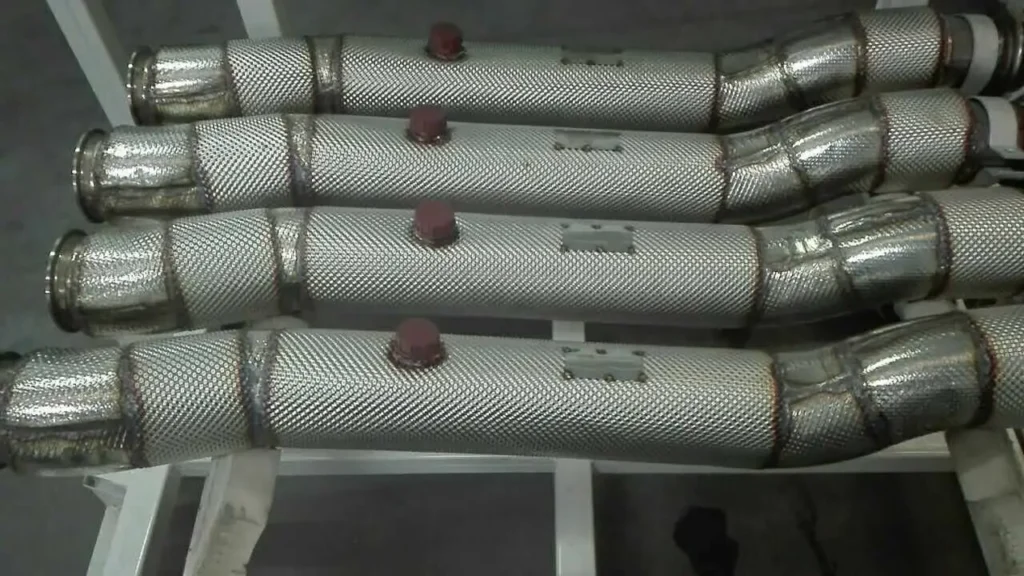

The exhaust system, which includes components like the exhaust manifold and the catalytic converter, also employs heat shields. These shields prevent the high temperatures generated by the exhaust gases from damaging other parts of the vehicle, such as the undercarriage, fuel lines, and electrical wiring. Furthermore, they protect the car’s occupants from heat that could otherwise make its way into the cabin.
Heat shields are typically constructed from durable, heat-resistant materials. Sheet metal, often made of stainless steel, is a common choice due to its ability to reflect heat and its high melting point. Stainless steel can withstand temperatures up to 1500°F (815°C) without losing its structural integrity. This makes it an ideal shield material for areas exposed to extreme heat, such as near the exhaust manifold or catalytic converter.
However, the choice of material can vary depending on the specific requirements of each part of the vehicle. Some shields may incorporate other materials, such as ceramics or composites, to provide additional insulation or to cope with particularly high temperatures.
In summary, car heat shields play a vital role in protecting your vehicle and its occupants from excessive heat. Whether they’re made from sheet metal, stainless steel, or other materials, they help keep your car running smoothly and safely. As we delve deeper into this topic, we’ll explore the specific benefits and drawbacks of these materials, and how they’re used in different parts of the car.
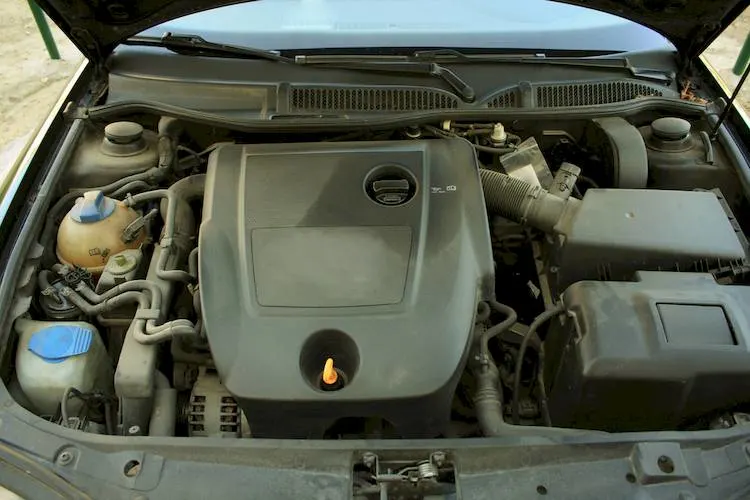

Heat shields play a vital role in ensuring the smooth and safe operation of vehicles, but are often overlooked. Beneath the smooth metal plates that form the car’s appearance is a complex network of components that generate and withstand a lot of heat. One of the most critical tasks of these components is to manage and mitigate excessive heat generated by the engine and exhaust system. The engine and exhaust system are the main heat sources of the car.
For example, exhaust manifolds and catalytic converters operate at high temperatures due to the heat generated by fuel combustion. Without proper management, these exhausts can damage vehicle components, reduce efficiency, and even pose a hazard to passengers. This is where the car heat shield comes into play.
Heat shields are typically made of stainless steel, a material highly prized for its durability and heat resistance, which protects sensitive parts of a vehicle from the extreme heat generated by the exhaust system. Stainless steel has a melting point of about 1,400 to 1,550 degrees Celsius (2,550 to 2,820 degrees Fahrenheit), making it an ideal thermal barrier that can protect the rest of the car from the high temperatures of exhaust manifolds and catalytic converters.
These heat barriers effectively block radiant heat from reaching other components and the interior of the car. By reflecting or radiating heat, they prevent damage to the vehicle’s components and ensure passenger comfort. The technical parameters of these shields, such as their thermal conductivity (stainless steel is about 16.2 W/m-K at room temperature), give us insight into how they manage heat transfer. This low thermal conductivity means that stainless steel does not easily allow heat to pass through, making it an excellent material for this job.
In addition, the role of the heat shield is to protect the car from flammable substances that exhaust fumes may ignite, such as oil or grease that may accumulate under the car. By keeping the exhaust system at a safe distance from these inflammables, the shield adds an extra layer of safety to the operation of the car. In short, the car’s heat shield is the unsung hero, providing protection against excessive heat generated by the engine and exhaust. They ensure that the heat of the car is kept at a controlled level, protecting the performance of the vehicle and the safety of the passengers from the potential dangers of high temperatures and heat transfer.
Learn More About: Do you need a heat shield on your car?
Analysis of Heat Shield Materials
When it comes to heat shield materials, it’s essential to consider their thermal insulation properties. These properties determine how well the material can prevent heat transfer, a crucial factor in protecting car components and passengers from excessive heat.
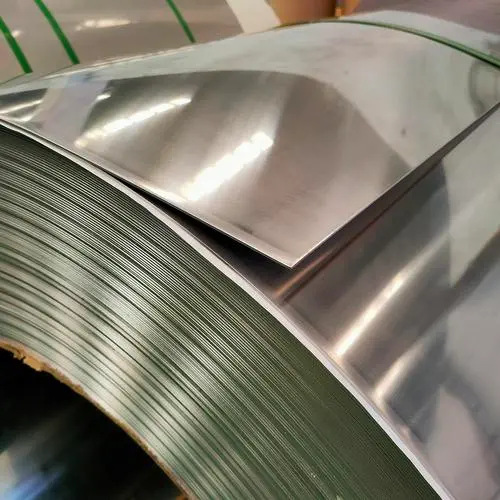

First, let’s discuss sheet metal, particularly stainless steel. It’s a popular choice for heat shields due to its high melting point, around 1500°F (815°C), and its ability to reflect radiant heat. However, stainless steel doesn’t have the best thermal insulation properties. It can conduct heat quite efficiently, meaning heat can still pass through it to some extent.
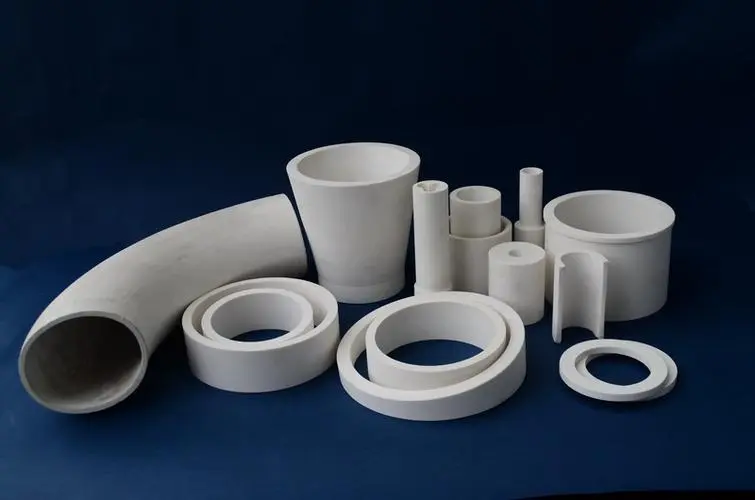

On the other hand, ceramic materials offer superior heat insulation. They have low thermal conductivity, making them excellent at preventing heat transfer. Ceramics can withstand temperatures exceeding 2000°F (1093°C), making them suitable for high-heat areas like the exhaust manifold. However, ceramics are more brittle than metals, which can lead to durability issues.
Aluminum foil composite materials, which combine the strengths of various materials, are also used. For example, a composite heat shield might consist of a sheet metal outer layer for reflection and a ceramic inner layer for insulation. This combination can provide both durability and excellent thermal insulation.
So, which material is the best for heat shields? Well, it depends on the specific application. For instance, stainless steel might be the best choice for an under-car heat shield due to its durability and sufficient heat reflection. But for an exhaust manifold heat shield, a ceramic or composite material might be more suitable due to their superior thermal insulation properties.
In all cases, the goal is to create a thermal barrier that can withstand and insulate against the heat generated within a car. The choice of material is critical in achieving this, as it directly impacts the heat shield’s effectiveness.
In conclusion, while there isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer, understanding the properties and capabilities of each material can guide us to make the best choice for each application. Whether it’s stainless steel, ceramic, or a composite, the right material can make a significant difference in the performance and safety of a vehicle.
View our products: Aluminized Fabric
Heat Shields in Different Parts of the Car
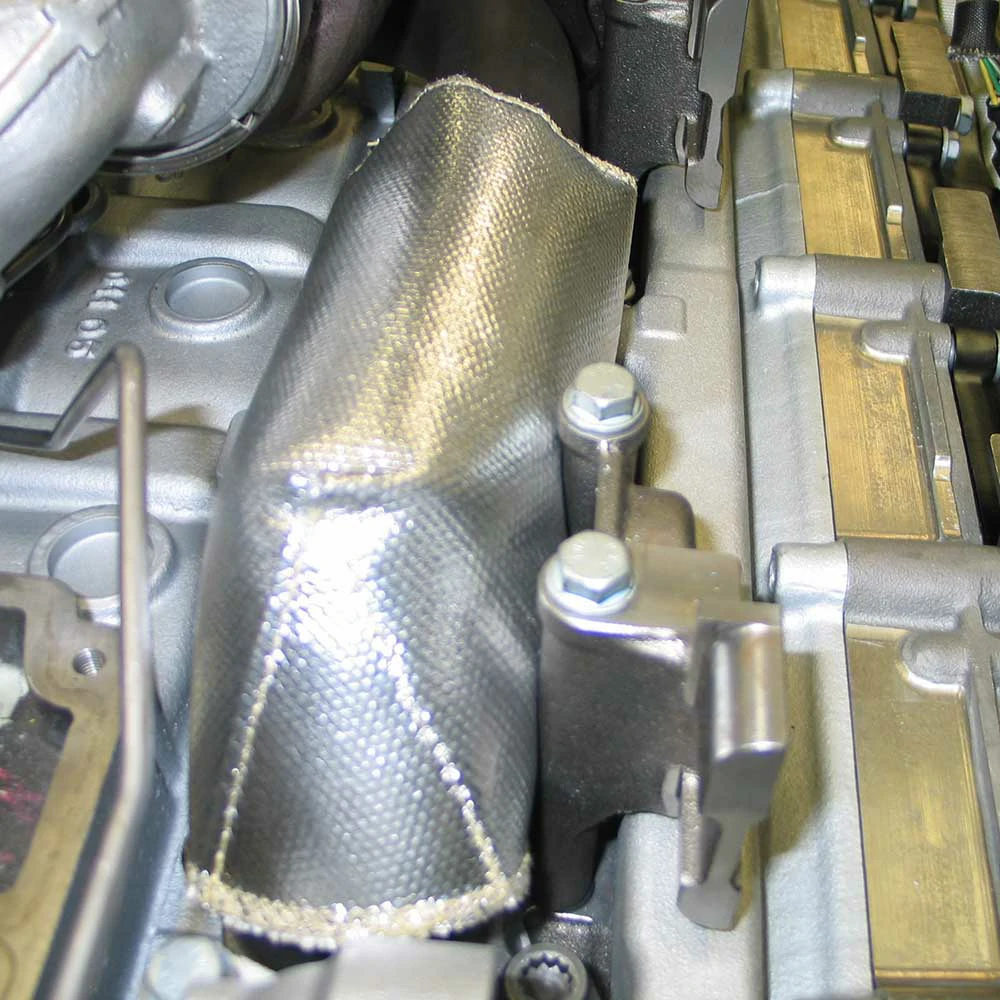
Heat shields play a crucial role in different parts of a car, including the exhaust system and the undercarriage. Let’s delve into their specific roles and material choices in these areas.
In the exhaust system, heat shields insulate exhaust pipes to prevent heat transfer to other components and the car’s interior. Exhaust pipes can reach temperatures of up to 1200°F (650°C), especially near the exhaust manifold and catalytic converter. Here, materials like ceramics or aluminum foil composites fabric , known for their superior heat insulation properties, are commonly used. These materials can withstand extreme temperatures while effectively reducing heat transfer.
For the undercarriage, heat shields protect the car’s underside from heat radiating from the exhaust system. They also shield fuel lines, electrical wiring, and other sensitive components from heat damage. Stainless steel, with its high melting point and good heat reflective properties, is often the material of choice here. It offers a balance of durability and sufficient heat protection.
However, heat shields are not without their issues. A common problem is a burning smell, which can occur if debris like leaves or plastic bags get caught on a hot exhaust shield. Over time, heat shields can also become loose due to wear and tear or corrosion. A loose heat shield can create a rattling noise, especially when the car is in motion.
Auto repair costs for heat shield issues can vary widely based on the specific problem and the car model. On average, replacing a heat shield can cost anywhere from $100 to $400, including parts and labor. Of course, these are average figures, and actual costs can vary based on local labor rates and the complexity of the repair.
Heat shields in different parts of a car play vital roles in insulating against heat and protecting the vehicle’s components. Despite potential issues like burning smells or loose shields, their benefits far outweigh these challenges. Regular inspections and timely repairs can ensure they continue to function effectively, keeping your car safe and performing at its best.
The Future of Car Heat Shields: Heat Reflective Material
Heat reflective materials are shaping the future of car heat shields. These materials, known for their excellent heat reflection capabilities, offer a multitude of benefits.
Heat reflective materials work by bouncing back radiant heat, instead of absorbing it. This characteristic significantly reduces the temperature of the protected area. In cars, this means less heat transfer to sensitive components, resulting in improved performance and longevity.
The benefits of heat reflective materials extend beyond cars. They have a wide range of applications, including fire pits. By reflecting heat, these materials prevent the pit’s exterior from becoming too hot, enhancing safety. This versatility showcases the potential of heat reflective materials in various heat management situations.
Now, let’s turn our attention to WT, a company making strides in heat reflective materials for car heat shields. They have developed a new composite material that reflects up to 95% of radiant heat. This is a significant increase from traditional materials like stainless steel, which typically reflect around 60% of radiant heat.
WT’s aluminum foil material is also lightweight, reducing the overall weight of the car, which can improve fuel efficiency. Moreover, it’s highly durable and resistant to corrosion, offering a longer lifespan compared to traditional heat shield materials.
Heat reflective materials represent the future of car heat shields, offering superior heat reflection and durability. Companies like WT are leading the way with innovative materials that promise to enhance the performance and safety of our vehicles. As we move forward, we can expect to see a wider adoption of these materials, not just in cars, but in a broad range of heat management applications.
Traditional materials, like stainless steel, have served us well. But the future lies in the adoption of advanced heat reflective materials. These materials, capable of reflecting up to 95% of radiant heat, offer superior protection. They also provide added benefits, like weight reduction and corrosion resistance.
Among the pioneers in this field, WT stands out with its innovative heat reflective material. This material not only enhances car performance but also extends the lifespan of the components.
Now, isn’t that something worth exploring further? We encourage you to delve deeper into the world of heat reflective materials. Learn more about the groundbreaking work WT is doing. It’s not just about improving cars; it’s about shaping the future of heat management across a wide range of applications. So, let’s embrace this future together, one heat shield at a time.




