Introduction
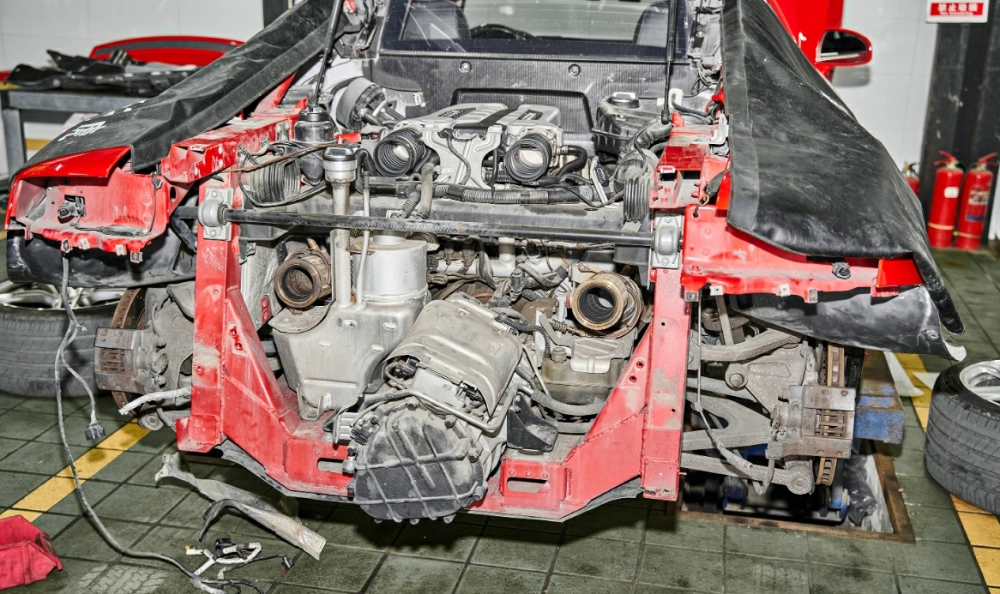

In diverse industries worldwide, heat shields play a pivotal role, particularly in the realm of automotive engineering. A heat shield on a car is more than just a component; it’s a critical part of thermal management, designed to control and regulate temperatures. From spacecraft to the humble family car, heat shields are universally employed to safeguard systems from excessive heat.
Diving into the specifics, let’s consider the engine bay of a car. This area houses numerous internal components, each playing a unique role in the vehicle’s operation. However, these components can be vulnerable to the extreme temperatures produced by the engine. This is where the heat shield steps in. It acts as a guardian, preventing heat damage to the bodywork and preserving the integrity of these internal components.
Understanding Heat in Automotive Contexts
Heat is a byproduct of various processes within a car, and managing it is crucial for both performance and safety. The primary sources of heat in a vehicle include the engine, exhaust system, and turbochargers. The engine, for example, can generate temperatures exceeding 200 degrees Fahrenheit during operation, while the exhaust system can reach even higher temperatures, often surpassing 750 degrees Fahrenheit. Turbochargers, due to their high-speed rotating components and the compression of air, also contribute significantly to the overall heat output.
The impact of heat on car components is profound. Electronics, such as ECUs and sensors, can malfunction if exposed to excessive heat. Fuel lines may deteriorate faster, potentially leading to leaks. Wiring insulation can melt, increasing the risk of electrical shorts and fires. Moreover, high temperatures can cause certain plastics and rubbers to become brittle or degrade, affecting the longevity and reliability of various parts.
Uncontrolled heat poses several risks. Engine overheating can lead to reduced performance, increased wear, and in severe cases, engine failure. It can also cause coolant to boil over, creating hazardous conditions under the hood. Fire hazards are another serious concern; a small spark in the presence of leaking fuel or oil can ignite, leading to a vehicle fire.
The Importance of Heat Shields in Cars
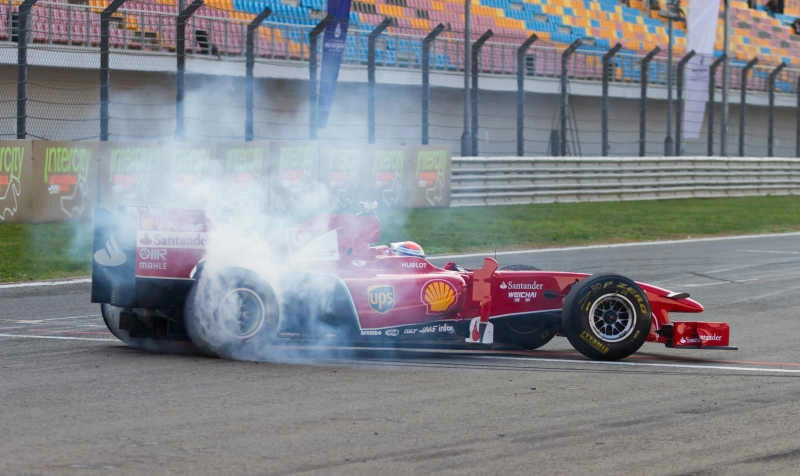

Where temperatures can soar up to 2000 degrees Fahrenheit (1093 degrees Celsius) during high-performance conditions. The engine, as the heart of the vehicle, is a major heat source, and managing this heat is crucial. This is where heat shields, the unsung heroes of thermal management, come into play.
Heat shields work by reducing under-hood heat and intake air temperature. The engine’s optimal performance is achieved when the intake air temperature is around 68 to 86 degrees Fahrenheit (20 to 30 degrees Celsius). However, without a heat shield, the intake air temperature can rise up to 140 degrees Fahrenheit (60 degrees Celsius) or more, which can significantly reduce engine efficiency.
Hot air is less dense than cool air, meaning it contains fewer oxygen molecules for the combustion process. A 10-degree increase in intake air temperature can lead to a 1% decrease in engine power output. By reducing the intake air temperature, heat shields ensure the engine receives a denser, oxygen-rich air supply, thereby enhancing combustion and overall engine performance.
Now, let’s consider the potential risks of an exposed engine block without a heat shield. The engine oil, designed to function optimally at temperatures between 180 to 200 degrees Fahrenheit (82 to 93 degrees Celsius), could overheat and lose its viscosity. This could result in inadequate lubrication, causing the engine components to wear out faster. Moreover, the high temperature could cause the paint on the engine block to emit a burning smell, a clear sign of overheating.
Furthermore, without a heat shield for a car, the radiant heat from the engine block could damage nearby components. For instance, the plastic parts in the engine compartment, which can start to deform at temperatures as low as 248 degrees Fahrenheit (120 degrees Celsius), are at risk. This could lead to mechanical failures, costly repairs, and even safety risks.
Heat shields are not just optional accessories but integral components in a car. The heat shield for a car plays a vital role in thermal management, ensuring optimal engine performance and safety by effectively dissipating excessive heat. By reducing under-hood heat and maintaining optimal intake air temperature, they contribute to the longevity and performance of the vehicle while preventing potential risks like a burning smell from an overheated engine block.
The Benefits of Fabricated Heat Shields
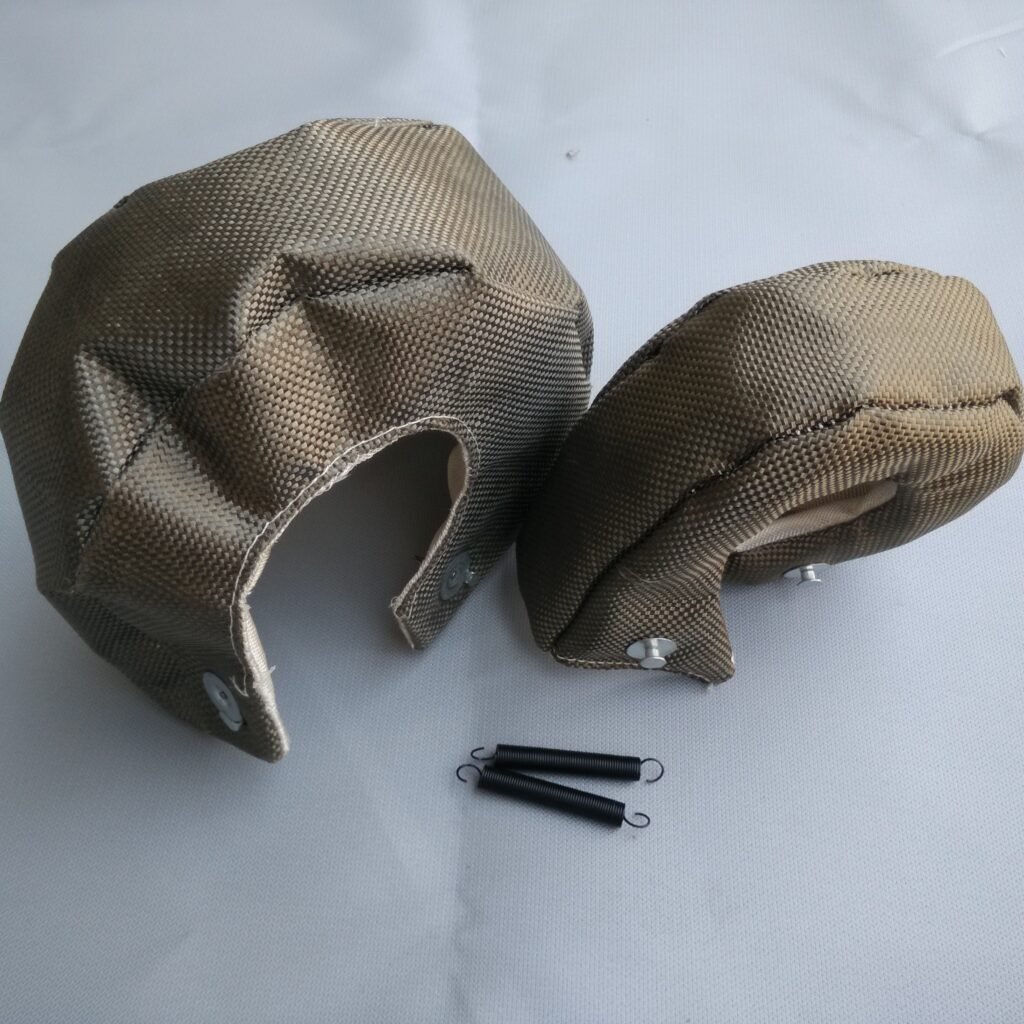

Fabricated heat shields are a game-changer in the automotive industry. These specialized shields offer a myriad of benefits, including a reduction in engine block weight and increased fuel efficiency.
By replacing traditional, heavier heat shields with fabricated ones, we can significantly reduce the weight of the engine block. For example, an aluminum fabricated heat shield weighs around 2.7 g/cm³, significantly less than a steel shield, which can weigh up to 7.85 g/cm³. This weight reduction can lead to improved fuel efficiency, as less energy is required to move a lighter vehicle.
Beyond weight reduction, fabricated heat shields play a vital role in thermal management within the engine bay. High temperatures can cause engine timing variations, leading to long-term performance reductions. A fabricated heat shield can reduce this heat by reflecting up to 90% of radiant heat, keeping the engine running smoothly and consistently.
Shielding specific components within the engine bay yields similar benefits. For instance, protecting the air intake system and engine mount vents can ensure optimal performance. By keeping the air intake cool, we can prevent power loss and improve fuel efficiency. Similarly, shielding the engine mount vents can prevent heat damage to these essential components.
Moreover, fabricated heat shields are particularly useful near the exhaust manifold and the catalytic converter, two of the hottest parts of a vehicle. By effectively managing the extreme heat these components produce, we can prevent heat damage and ensure the longevity of surrounding parts.
Fabricated heat shields offer a multitude of benefits, from weight reduction and improved fuel efficiency to enhanced thermal management. By shielding specific components, we can ensure optimal performance and longevity of the vehicle. As we continue to innovate, the use of fabricated heat shields in the automotive industry will undoubtedly become more prevalent.
Types of Heat Shields: Fixed vs. Flexible
When it comes to heat shield for a car, there are two main types to consider: fixed (rigid) and flexible. Both have their own unique advantages and are designed to suit different applications within the vehicle.
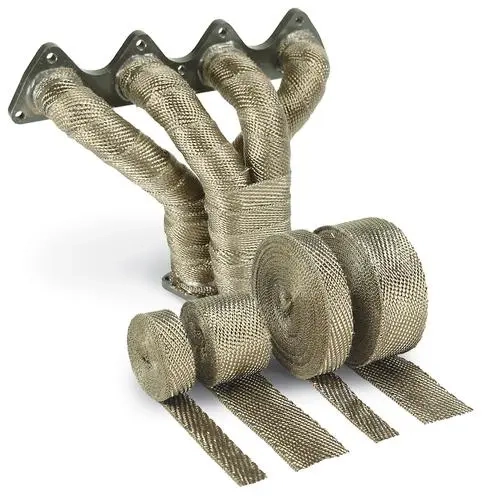

Fixed heat shields, as the name suggests, are rigid and typically bolted directly to the engine block or exhaust system. Fixed car heat shield are often made from aluminum, a material known for its excellent thermal properties. Aluminum can reflect up to 95% of radiant heat, making it an ideal material for fixed heat shields. Additionally, aluminum’s light weight, about 2.7 g/cm³, is a bonus, contributing to overall vehicle weight reduction.
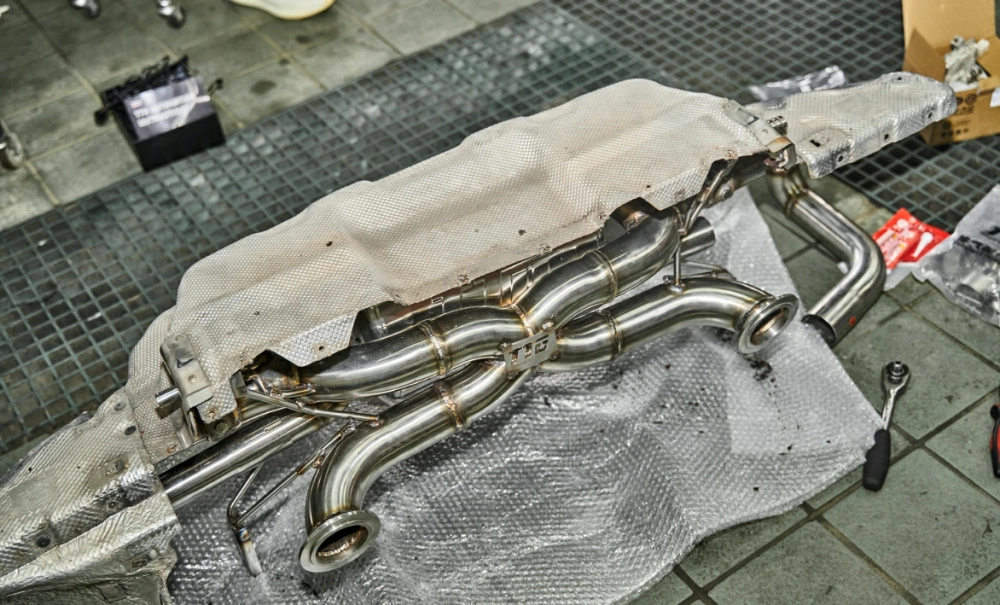

On the other hand, flexible heat shields are more adaptable, able to conform to irregular shapes and spaces within the engine compartment. Like their fixed counterparts, flexible heat shields are also commonly made of aluminum. However, they are often combined with other materials like fiberglass or silica, which can withstand temperatures up to 2000 degrees Fahrenheit (1093 degrees Celsius).
Now, let’s debunk a common misconception about heat shield materials. Many people associate thicker, denser materials with greater thermal capacity. However, the thermal barrier effectiveness of a heat shield is less about its thickness and more about its reflective properties and heat dissipation. For instance, an aluminum heat shield of just 0.1 inches (2.54 mm) thickness can effectively reflect most of the radiant heat.
In conclusion, whether fixed or flexible, the choice of heat shield in a car depends on the specific requirements of the engine compartment. Aluminum, with its excellent thermal properties, lightweight, and versatility, proves to be a superior material choice for both types of heat shield for a car. And remember, it’s not the thickness but the material’s ability to reflect and dissipate heat that truly makes a heat shield effective.
Refer To:What is the heat shield in a car?
The Rise of Thermal Textiles in Automotive Insulation
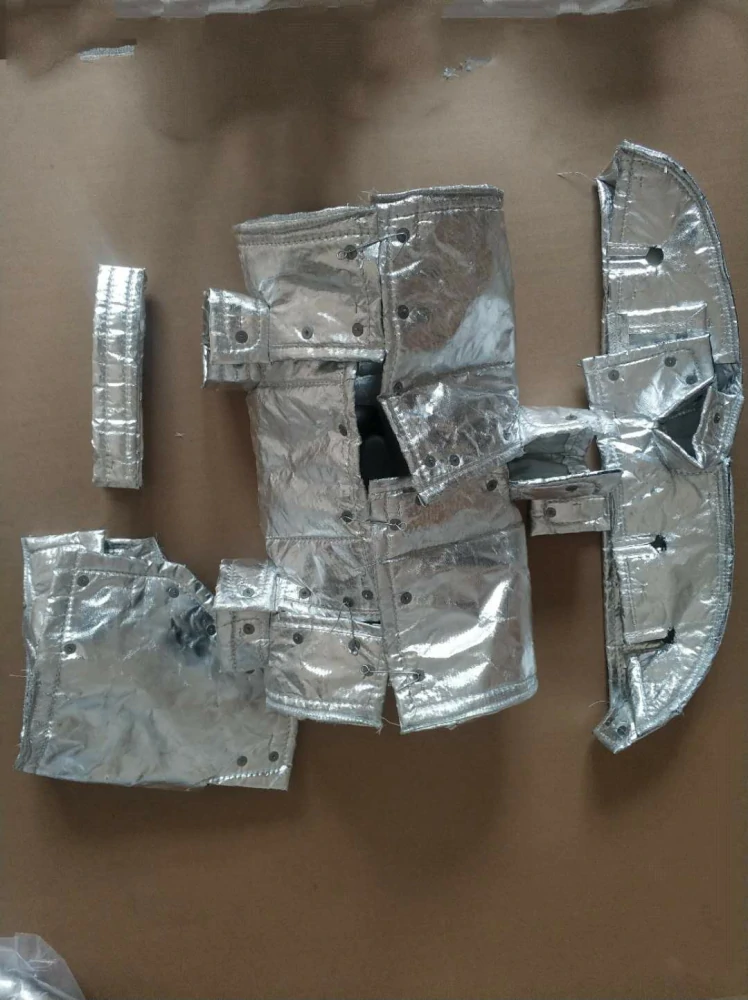

The automotive industry is continuously evolving, always seeking innovative materials and solutions to enhance performance and safety. A recent trend is the increasing use of thermal textiles for automotive insulation, particularly within exhaust systems. Exhaust systems are a hotspot for extreme heat, reaching temperatures up to 1200 degrees Fahrenheit (649 degrees Celsius).
Thermal textiles, made from materials like fiberglass or silica, have emerged as effective thermal barriers in these high-heat engine environments. These fabrics can withstand extreme heat, with silica fabrics remaining stable even at temperatures up to 1800 degrees Fahrenheit (982 degrees Celsius). This makes them ideal for insulating exhaust systems, protecting surrounding components from heat damage.
In addition to their high temperature resistance, these textiles often come with proprietary coatings. These coatings enhance the fabric’s heat reflecting capabilities, adding another layer of protection. For instance, a coating of aluminum on a fiberglass fabric can increase heat reflection by up to 90%, significantly reducing the radiant heat reaching nearby car components.
But the benefits of thermal textiles in exhaust systems don’t stop there. These materials are lightweight, with fiberglass fabric weighing around 0.5 to 2.0 oz/sq yd (17 to 68 g/sq m), contributing to overall vehicle weight reduction. Additionally, these fabrics are flexible, allowing them to conform to the intricate shapes within the engine environment.
The rise of thermal textiles in automotive insulation is a testament to the industry’s commitment to innovation. By effectively managing extreme heat within exhaust systems, these high-temperature fabrics enhance vehicle performance and safety. As technology advances, we can expect to see even more applications of these versatile materials in the automotive world.
Learn More About:What Material Is Used For A Car Heat Shield?
Looking ahead, the future of heat shields in the automotive sector is bright. As the industry pursues the balance of key performance indicators (KPIs), the focus on thermal management will continue to grow. Reducing engine block weight, improving fuel efficiency, and preventing performance reductions are all critical goals. Achieving these objectives will produce vehicles that not only perform better but also appeal more to end-users.
Heat Shields and Vehicle Regulations
When it comes to car heat shield, there are specific legal requirements and safety standards that must be adhered to. These regulations are designed to ensure that vehicles operate safely and do not pose a risk to their occupants or other road users due to excessive heat.
In the United States, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) sets federal motor vehicle safety standards (FMVSS), which include guidelines for fire prevention and the protection of vehicle components from heat. For example, FMVSS 302 mandates the flame resistance of interior materials, indirectly affecting the need for effective heat shielding to prevent interior fires.
The importance of using heat shields that comply with local regulations cannot be overstated. Non-compliance can lead to safety issues, legal consequences, and potentially void insurance claims in the event of a heat-related incident. Additionally, vehicles that do not meet the required safety standards may be deemed unfit for road use.
Manufacturers of car heat shields must also comply with regulations, ensuring that their products meet the necessary thermal protection specifications. This includes using materials that can withstand high temperatures and have been tested to perform effectively in various automotive applications.
What are the common materials used for heat shields under a car's bonnet?
Common materials include aluminum, stainless steel, ceramic coatings, and heat-resistant fabrics. These materials are chosen for their ability to reflect or dissipate heat away from sensitive components.
Why is a heat shield important under a car's bonnet?
Heat shields are important because they protect vital parts such as wiring, hoses, and electronics from heat damage, which can lead to premature aging, reduced performance, or failure. They also help in maintaining the overall efficiency of the engine and can improve the vehicle’s cooling system performance.
Can a missing or damaged heat shield cause problems with my car?
Yes, a missing or damaged heat shield can lead to overheating of components, increased risk of fire, and potential damage to the engine or exhaust system. It can also affect the comfort inside the cabin by allowing more heat to penetrate through to the passenger area.
How can I tell if my car's heat shield is damaged or needs replacement?
Signs of a damaged heat shield include visible rust or holes in the shield, unusual noises from the engine compartment, or a noticeable increase in engine compartment temperatures. Regular inspections during maintenance checks can help identify issues early.
Is it safe to drive with a missing or damaged heat shield?
Driving with a missing or damaged heat shield is not recommended as it can lead to component failure and potentially dangerous situations. It’s best to have the heat shield repaired or replaced as soon as possible.
Are there different types of heat shields for different parts of the engine compartment?
Yes, there are various types of heat shields designed to protect specific areas or components, such as those for the exhaust manifold, turbocharger, or fuel lines. The design and material can vary based on the heat levels and the function of the part being protected.
Where can I purchase a heat shield for my car?
Heat shields can be purchased from automotive parts stores, online retailers, or directly from the vehicle manufacturer. It’s important to choose a heat shield that is compatible with your vehicle and the specific area you need to protect.


