The Role of Heat Shield Materials in Various Industries
Heat shield materials are crucial in protecting against high temperatures. They are not just barriers but are carefully designed to provide thermal insulation and block heat effectively. This article explores the importance of heat shield materials, their principles, technical parameters, and their impact on industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and industrial settings.
Heat Shield Materials: Engineering Solutions for Thermal Protection
Heat shield materials are engineered to protect against high temperatures. They provide thermal insulation and effectively block heat. These materials are essential in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, construction, and industrial settings.
Technical Parameters of Heat Shield Materials
The effectiveness of heat shield materials depends on several technical parameters. These include thermal conductivity, which measures how well a material conducts heat; specific heat capacity, indicating how much heat a material can absorb before increasing in temperature; and emissivity, which determines how well a material radiates heat. Additionally, the material’s melting point and thermal expansion properties are critical factors in determining its suitability for high-temperature applications.
The Impact of Heat Shield Materials on Industry
Heat shield materials have a transformative impact on various industries. In the automotive sector, they protect engines and exhaust systems, enhancing performance and safety. In aerospace, they are vital for protecting spacecraft during re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere. In construction, they are used in insulation to improve energy efficiency and comfort. Industrial settings benefit from heat shield materials by protecting equipment and workers from high temperatures, ensuring safety and productivity.
Conclusion: The Essential Role of Heat Shield Materials
In conclusion, heat shield materials are indispensable in protecting against high temperatures. Their ability to provide thermal insulation and block heat makes them vital in various industries, from automotive to aerospace, construction, and industrial settings. The careful engineering and selection of these materials ensure optimal performance, safety, and efficiency in high-temperature environments.
What Can Be Used as a Heat Shield
Aluminum Heat Shields: Efficient Protection Against Radiant Heat
Shielding materials protect technologies and personnel from extreme heat. Aluminum heat shields are effective due to their high reflectivity and low thermal mass. These lightweight, robust solutions are ideal for thermal insulation, especially in automotive exhaust heat management.
Comparing Heat Shield Materials
The effectiveness of heat shields depends on their ability to withstand high temperatures and provide thermal insulation. Aluminum heat shields can reflect up to 90% of radiant heat and endure temperatures up to 650°C. Fiberglass and ceramic materials offer superior thermal insulation, handling continuous exposure to temperatures as high as 1000°C, making them suitable for extremely hot environments.
Common Heat Shield Material Table
| Material Name | Temperature Resistance (Max Temp °C) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K at room temp) | Characteristics | Application Fields |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | 650 | 205 – 250 | Lightweight, excellent reflectivity, corrosion resistant | Automotive heat shields, kitchen foil, electronic heat sinks |
| Fiberglass | 540 | 0.04 – 1.0 | Non-conductive, fire-resistant, good tensile strength | Building insulation, protective clothing, electrical insulation |
| Ceramic Insulation | 1000+ | 1 – 10 | Low thermal conductivity, high temperature and chemical stability | Aerospace, industrial furnaces, kiln linings |
| Aerogel | 650 | 0.013 – 0.015 | Extremely low density, excellent thermal insulator | Spacecraft thermal insulation, cryogenics, apparel |
| Carbon-Carbon Composite | 2500+ | 5 – 7 | High strength-to-weight ratio, high thermal stability | Aerospace (rocket nozzles, leading edges), Formula 1 braking systems |
| Phenolic Impregnated Carbon Ablator (PICA) | 1850 | 0.25 | Lightweight, ablative resistance to extreme heat | Spacecraft re-entry heat shields, nose cones |
| Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) | 1316 | 5 – 15 | High modulus of elasticity, low thermal expansion, withstands thermal shock | Space Shuttle nose caps, wing leading edges |
| Stainless Steel | 870 – 1400 (depending on grade) | 14 – 25 | High tensile strength, corrosion resistance, maintains strength at high temperatures | Industrial ovens, automotive exhaust systems, kitchen appliances |
| Reflective Coatings | Varies with base material | – (coating itself is a thin layer with negligible conductivity) | Reflects radiant heat, can be applied to various substrates | Buildings (radiant barriers), protective clothing, automotive |
| Exhaust Heat Wraps | ~815 | – (varies, designed to insulate rather than conduct heat) | Reduces heat loss from exhaust system, improves engine performance | Automotive exhaust systems, motorcycle exhaust pipes |
the Importance of Heat Shield Material
Efficacy of Heat Shields in Controlling Heat Transfer
Heat shields are effective because they control and reduce heat transfer, creating safer and more sustainable environments. For example, a heat shield can reduce heat transfer by 80%.
How Heat Shields Work
Heat shields work by insulating and reflecting heat. Placed near heat sources, they prevent direct heat transfer to sensitive parts. Materials with good reflective properties bounce radiant heat away, protecting the surroundings.
Thermal Conductivity of Heat Shield Materials
The thermal conductivity of a material, measured in watts per meter-kelvin (W/m·K), is crucial. High-quality aluminum foil composite, for instance, has a low thermal conductivity of 1.5 W/m·K, minimizing heat conduction.
Benefits of Reduced Heat Transfer
Reducing heat transfer ensures component safety and improves energy efficiency. By blocking heat effectively, these materials help machinery and systems operate better, reducing overheating risk and enhancing performance.
Importance of Heat Shields in Various Industries

Risks of Neglecting Heat Shields in Industries
Failing to use heat shields in industries poses significant risks. In automotive settings, without heat shields, critical components like fuel lines can overheat, reducing efficiency and safety. Similarly, in aerospace, inadequate heat shields during re-entry can jeopardize structural integrity and mission success.
Impact on Construction and Industrial Settings
In construction, the absence of heat shields increases cooling costs and reduces building sustainability. Industrial environments without heat shields face accelerated wear, inefficiencies, and safety hazards.
The Crucial Roles of Heat Shields
Heat shields are vital for protecting automotive systems, ensuring aerospace safety, promoting energy efficiency in construction, and sustaining industrial equipment. Tailored solutions like aluminum foil composites fabrics and phenolic boards mitigate risks, enhance safety, and optimize efficiency across various sectors.
Automotive Industry
Aluminum and Beyond in Automotive Protection

Aluminum Heat Shields in Automotive Design
In automotive design, heat shield material is crucial for protecting vehicles from high heat. Aluminum heat shields are particularly efficient for thermal insulation.
Protecting Undercarriage and Engine Components
Aluminum heat shield material is designed to shield the undercarriage and engine components. It must withstand high temperatures and deflect the intense heat from engines and exhaust systems, ensuring both vehicle performance and passenger safety.
Learn more: What Material Is Used For A Car Heat Shield?

Aluminum's Superiority in Heat Shielding
Aluminum is excellent for heat shielding due to its ability to reflect 97% of thermal radiation and its malleability. This allows it to be shaped into intricate designs to protect vulnerable vehicle parts, from the exhaust system to the engine bay.
Precision Engineering with Aluminum
Aluminum heat shields are precision-engineered to fit the unique contours of each vehicle model. They can be cut, bent, and adapted to ensure every part is protected from high heat, enhancing overall vehicle performance.
Comparing Aluminum to Stainless Steel
While stainless steel is robust at high temperatures, it cannot match aluminum’s versatility and lightweight properties. Aluminum’s superior insulating capabilities contribute to vehicle aerodynamics and fuel efficiency
Innovations in Aluminum Composites
Emerging innovations, including nanotechnology, are enhancing aluminum composites for heat shielding. These advancements are tailored to the needs of next-generation vehicles, including electric models with specific thermal management requirements.
Aircraft And Spacecraft
Heat Shield Material, Aluminum Heat Shield Material, and Heat Shielding Material

In the realm of aerospace engineering, the heat shield material plays a vital role in mission success. Aluminum heat shield material, renowned for its lightweight and reflective properties, is a cornerstone in the design of heat shields. These shields are meticulously designed to protect spacecraft from the punishing conditions of space travel.
aluminum heat shield material

Incorporating aluminum foil composites, heat shield materials exhibit remarkable thermal radiation reflectivity, essential in repelling the intense thermal energy encountered during re-entry. Aluminum heat shield material can resist temperatures reaching 600°C, with a thermal conductivity often as low as 2.0 W/m·K, making it a stalwart barrier against high heat.
Stainless Steel

Beyond aluminum, stainless steel often complements as a robust insulating material, especially when facing temperatures that exceed the aluminum’s threshold. It’s not uncommon for stainless steel to sustain functionality at high temperatures, up to 1,000°C, contributing significantly to the thermal insulation strategy.
| Material | Max Temp Resistance | Thermal Conductivity | Density |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Foil Composites | 600°C | 2.0 W/m·K | 2.7 g/cm³ |
| Stainless Steel | 1,000°C | 15 W/m·K | 8.0 g/cm³ |
Synergy Of Materials
The synergy of materials, including the aluminum heat shield coupled with insulating layers, ensures comprehensive thermal management. This multilayer approach allows for each heat shield to be designed with redundancy, a principle starkly visible in the SpaceX Starship’s strategy. Its surface is adorned with heat-resistant tiles, each functioning independently to offer continued protection even if one were to fail.
Reflecting on the iconic Space Shuttle, its heat shield boasted a repeating pattern of thermal protection tiles, each capable of withstanding high temperatures and multiple missions. This reusable heat shield strategy was a pioneering achievement in aerospace technology, offering a sustainable solution to the challenge of atmospheric re-entry.
Addressing challenges such as radiation exposure, extreme heat variations, and micrometeoroid impacts is central to advancing heat shield technology. Recent strides include the integration of nanotechnology, enhancing the resiliency and thermal resistance of shield materials. These advancements signify a leap toward more adaptive and dynamic heat shielding materials, capable of responding to the unpredictable conditions of space.
Construction (Roofing) Industry

Understanding the Need for Heat Shields in Construction
In the construction realm, the need for effective heat shields is paramount. Roofs, often exposed to direct sunlight, can absorb significant heat, leading to elevated interior temperatures, increased energy consumption, and potential discomfort for occupants. Heat shields play a crucial role in mitigating these challenges, providing thermal insulation and reflective properties designed to manage and block the ingress of radiant heat into the building structure.
Materials Commonly Used for Roofing Heat Shields
Reflective Aluminum Foil Composites
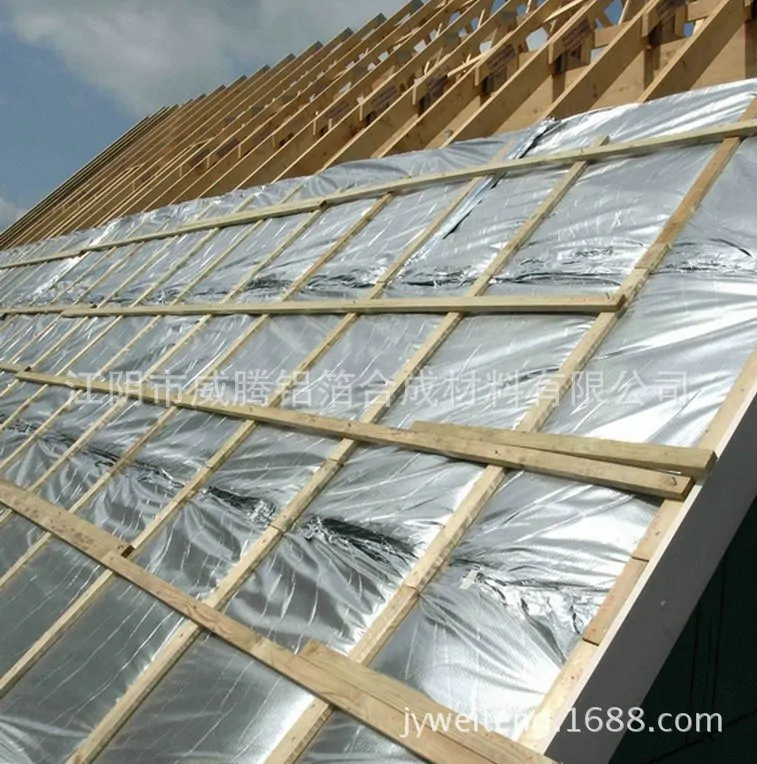

At the forefront of roofing heat shields are reflective aluminum foil composites. Engineered with precision, these materials boast high thermal radiation reflectivity, often exceeding 90%. Technical parameters include a low thermal conductivity of 1.8 W/m·K, ensuring efficient heat management. Applied as radiant barriers, these composites shield roofs from the sun’s intense rays, reflecting radiant heat away and maintaining a cooler interior environment.
Insulating Phenolic Boards

Complementing reflective composites, insulating phenolic boards contribute to comprehensive thermal insulation in roofing systems. With a low thermal conductivity of 0.03 W/m·K, these boards excel in blocking heat transfer. Their high-temperature resistance and durability make them ideal for withstanding prolonged exposure to sunlight and external weather conditions, enhancing the longevity of roofing structures.
Applications and Advantages in Roofing Systems
Roofing heat shields find versatile applications, particularly in regions with high temperatures or where energy efficiency is a priority. Reflective aluminum foil composites are applied beneath roofing materials, acting as a barrier against radiant heat. Phenolic boards, integrated into roofing structures, provide insulation, preventing the direct transfer of heat into the building.
The advantages are compelling. By incorporating heat shields, roofing systems contribute to reduced energy consumption for cooling, leading to lower utility costs. Additionally, the enhanced thermal management ensures a comfortable interior climate, promoting occupant well-being.
Sustainable and Energy-Efficient Heat Shield Solutions for Construction
In the pursuit of sustainable building practices, heat shield solutions are pivotal. Reflective aluminum foil composites and insulating phenolic boards align with green construction principles. These materials contribute to energy efficiency by reducing the reliance on air conditioning systems, lowering overall carbon footprints.
Beyond their immediate benefits, these heat shield solutions enhance the lifespan of roofing structures, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements. As the construction industry embraces sustainability, the incorporation of energy-efficient heat shields emerges as a fundamental step towards creating environmentally conscious and comfortable living spaces.
In conclusion, within the construction industry, heat shields redefine roofing dynamics, providing not only thermal insulation but also contributing to sustainable and energy-efficient building practices. Reflective aluminum foil composites and insulating phenolic boards epitomize the best in heat shield materials, elevating comfort and efficiency in roofing systems.
Industrial Applications

Diverse Applications of Heat Shields in Industrial Settings
In the vast landscape of industrial applications, heat shields emerge as indispensable guardians, designed to protect machinery and equipment from the relentless onslaught of high temperatures. From heavy manufacturing processes to maintenance of industrial facilities, the applications of heat shields are diverse, spanning sectors where thermal management is critical for optimal performance.
Materials Suitable for Industrial Heat Shields
Heavy-Duty Aluminum Foil Composite Materials:
Engineered for heavy-duty applications, aluminum foil composite materials lead the charge in industrial heat shielding. Their technical prowess includes a low thermal conductivity of 1.2 W/m·K and a maximum temperature resistance exceeding 600°C. These materials are designed to withstand the rigors of industrial environments, providing an effective barrier against heat transfer and ensuring the longevity of machinery.
Fire-Resistant Phenolic Boards:
In industrial settings where fire resistance is paramount, phenolic boards stand out as an ideal heat shield material. With a low thermal conductivity of 0.03 W/m·K and fire-resistant properties, these boards offer robust insulation. Their ability to endure high temperatures, reaching up to 300°C, makes them a reliable choice for applications demanding both heat resistance and thermal insulation.
Real-World Examples of Industrial Heat Shield Applications
Realizing the practical significance of industrial heat shields, consider their application in heavy machinery manufacturing. Aluminum foil composite materials, strategically placed around critical components, effectively block and reflect radiant heat, protecting machinery from overheating and ensuring optimal operational efficiency.
In industrial maintenance, the use of fire-resistant phenolic boards as heat shields enhances safety during repairs and upkeep. These boards insulate against high temperatures, safeguarding maintenance personnel and enabling more efficient and secure work environments.
Future Prospects and Evolving Needs in Industrial Heat Shielding
As industrial processes evolve and become more intricate, the needs in heat shielding continue to evolve. Future prospects include the integration of advanced materials with nanotechnology, promising even greater thermal resistance and durability. The demand for heat shields capable of adapting to dynamic temperature fluctuations, coupled with increased sustainability, is driving innovation in the industrial heat shielding landscape.
With an emphasis on energy efficiency, future industrial heat shields are likely to play a pivotal role in minimizing heat loss during manufacturing processes. As industries move towards greener practices, the integration of heat shields designed to reduce energy consumption aligns with global efforts to create more sustainable and environmentally conscious industrial practices.
In essence, industrial heat shields stand as silent sentinels in the realm of machinery and manufacturing, designed to protect, insulate, and ensure the efficient and safe operation of industrial processes. As technology advances, so too will the capabilities of heat shields, meeting the evolving needs of industries worldwide.
Other Industries
Exploration of Heat Shield Materials in Additional Industries
1. Electronics and Electrical Systems:
In the realm of electronics and electrical systems, managing heat is paramount for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Heat shields, crafted from advanced materials such as aluminum foil composites, shield delicate electronic components from the detrimental effects of high temperatures. These shields are designed to dissipate heat effectively, safeguarding sensitive circuitry and enhancing the reliability of electronic systems.
2. Renewable Energy Infrastructure:
The renewable energy sector, with its focus on sustainability, relies on heat shields to protect critical components in solar panels, wind turbines, and other infrastructure. Aluminum foil composites, known for their high thermal reflectivity and durability, are utilized to manage heat in solar panels, ensuring efficient energy conversion. In wind turbines, heat shields contribute to the longevity of electrical components, maintaining optimal performance in varying weather conditions.
3. Marine and Offshore Applications:
In the harsh marine and offshore environments, where exposure to saltwater and extreme temperatures is commonplace, heat shields become indispensable. Aluminum foil composite materials and phenolic boards, chosen for their corrosion resistance and durability, protect crucial components in marine vessels and offshore structures. These shields guard against the corrosive effects of saltwater and mitigate the impact of high temperatures on sensitive equipment.
Unique Challenges and Requirements in These Industries
In electronics and electrical systems, the challenge lies in managing heat generated by electronic components without compromising their functionality. The requirement is for heat shields that not only block heat effectively but also offer electrical insulation to ensure the safety and reliability of electronic systems.
Renewable energy infrastructure demands heat shields that can withstand the diverse weather conditions experienced by solar panels and wind turbines. Durability, resistance to environmental factors, and the ability to dissipate heat efficiently are critical requirements in this sector.
In marine and offshore applications, the unique challenge is combatting corrosion caused by saltwater exposure. Heat shields must be resistant to corrosion while effectively managing heat, ensuring the protection and longevity of equipment in maritime environments.
Customized Solutions Using Aluminum Foil Composite Materials and Phenolic Boards
Customized solutions for these diverse industries involve the strategic integration of aluminum foil composite materials and phenolic boards, each tailored to address specific challenges:
– Electronics and Electrical Systems: Aluminum foil composites, with their high thermal reflectivity, provide efficient heat management without compromising electrical integrity. These shields ensure the longevity of electronic components by blocking heat effectively.
– Renewable Energy Infrastructure: The durability of aluminum foil composites and the resistance of phenolic boards to environmental factors make them ideal for renewable energy applications. These materials protect against heat and corrosion, contributing to the sustained efficiency of solar panels and wind turbines.
– Marine and Offshore Applications: The corrosion-resistant properties of aluminum foil composites and phenolic boards make them well-suited for marine environments. These shields guard against the corrosive effects of saltwater, ensuring the reliability and safety of equipment in offshore settings.
In conclusion, heat shield materials prove to be versatile solutions, extending their protective embrace to diverse industries. Whether safeguarding electronics, fortifying renewable energy infrastructure, or withstanding the rigors of marine environments, customized solutions utilizing aluminum foil composite materials and phenolic boards contribute to the efficiency, longevity, and reliability of critical systems across these sectors.
In the intricate tapestry of diverse industries, the importance of heat shield materials resonates profoundly. These versatile solutions, designed to protect, manage heat, and provide thermal insulation, play pivotal roles across automotive, aerospace, construction, industrial, and other specialized sectors. From safeguarding sensitive electronic components to fortifying renewable energy infrastructure, the versatility of heat shield materials is undeniable. As guardians against radiant heat, they block, reflect, and dissipate high temperatures, ensuring the longevity, efficiency, and safety of critical systems.
In the realm of heat shield materials, WT stands as a beacon of innovation and reliability. As a professional manufacturer specializing in aluminum foil composite materials and phenolic boards, WT has been at the forefront of providing cutting-edge solutions to industries worldwide. The commitment to quality is reflected in the technical parameters of their products, such as high thermal radiation reflectivity, maximum temperature resistance, and low thermal conductivity. WT’s solutions go beyond shielding – they contribute to the efficiency and sustainability of processes, setting new benchmarks in the heat shield material industry.
The story of heat shield materials is one of resilience, adaptability, and progress. As we navigate the complexities of diverse industries, the significance of these materials in protecting components, managing heat, and ensuring operational efficiency cannot be overstated.
With WT leading the way, and a collective commitment to collaboration and innovation, the heat shield industry is poised to create a future where industries thrive under the protective embrace of cutting-edge heat shield solutions. Explore the possibilities, shield the future.
Where can I purchase heat shields?
Heat shields can be purchased from industrial suppliers, specialty retailers, or directly from manufacturers. It’s important to choose a reputable source that can provide products suited to your specific needs.
Can heat shields be used in both indoor and outdoor environments?
Yes, heat shields can be used in both indoor and outdoor environments. They are designed to withstand a variety of conditions, including exposure to the elements.
Are heat shields necessary in all industries?
Heat shields are necessary in industries where high temperatures pose a risk to equipment, workers, or the environment. This includes aerospace, automotive, industrial manufacturing, construction, energy production, and even consumer products.
What materials are commonly used for heat shields?
Common materials for heat shields include metals like aluminum and stainless steel, ceramics, high-temperature textiles, ablative materials, aerogels, and reflective coatings and foils.



