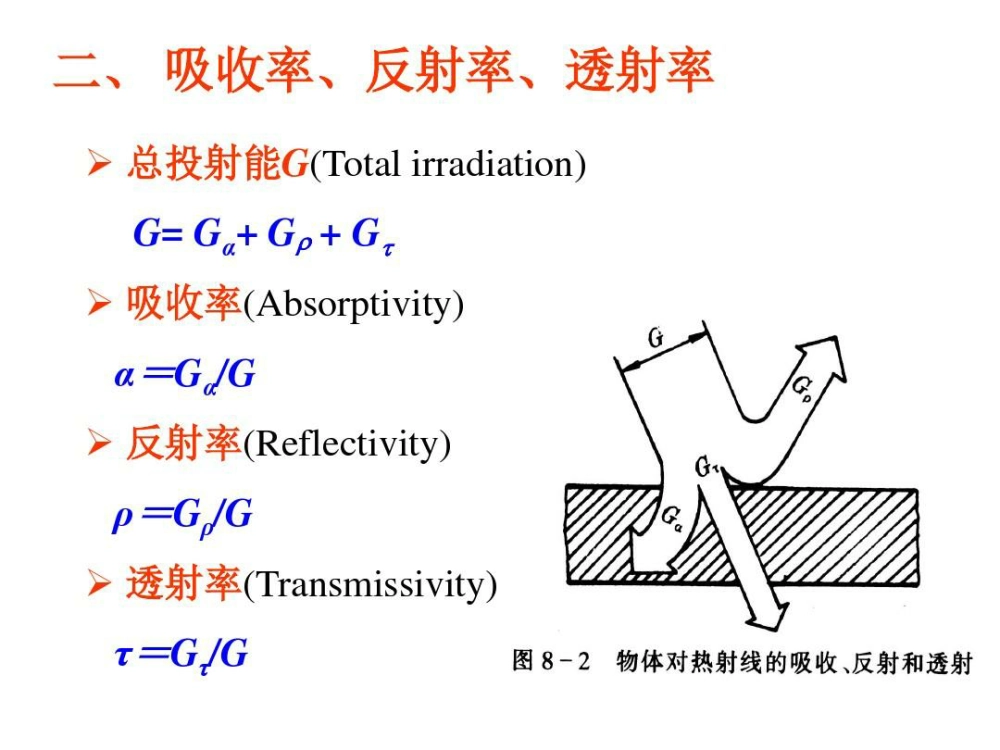
In the ever-evolving landscape of temperature control, the use of heat reflecting material has emerged as a crucial solution. These remarkable materials, meticulously designed to reflect radiant heat and mitigate heat transfer, offer an array of advantages that extend far beyond conventional insulation methods. In this all-encompassing guide, we will embark on a journey into the realm of heat reflective materials, unraveling their significance, merits, and wide-ranging applications. These materials, including highly reflective aluminum foil and reflective fabrics, serve as effective heat barriers and radiant barriers, reducing heat transfer and providing energy savings. They are used in various applications, from car covers and insulation materials to heat shields and reflective fabrics for high-temperature environments. By reflecting thermal radiation and reducing the need for air conditioners, these materials contribute to energy efficiency and help stay cool in hot conditions.
Heat Reflective Materials

In the world of construction, insulation, and energy management, heat reflecting material has become indispensable tools. These materials, known for their ability to deflect and reduce the transfer of heat, play a pivotal role in maintaining comfortable living and working environments. By creating an air space and utilizing materials like glass fiber, these heat reflective solutions effectively manage radiant heat, contributing to energy efficiency and reducing overall energy consumption.
Definition of Heat Reflective Materials
The functionality of heat reflective materials is grounded in the principles of reflectivity and heat transfer. When exposed to radiant heat, such as sunlight or infrared radiation, thermal insulating materials act as barriers, intercepting and reflecting a significant portion of the incoming heat. This process is akin to the way a mirror reflects visible light. In the case of heat reflective materials, they excel at reflecting heat energy while allowing minimal absorption.
High-quality heat reflective materials can achieve reflectivity values of up to 97%. This exceptional reflectance ensures that a substantial portion of radiant heat is deflected away, keeping the covered area cooler.
How Does Heat Reflective Material Work
Reflective insulation materials block radiant heat through a series of steps:
Exposure to Radiant Energy:
The material’s surface is first exposed to radiant energy, which is energy from a heat source like the sun.Interaction with Reflective Surface:
Radiant energy then interacts with the highly reflective surface, usually made of aluminum foil or a similar metallic coating.Reflection of Radiant Heat:
The reflective surface deflects most of the radiant heat away from the insulation.Creation of Air Space:
An air space next to the reflective surface acts as a thermal barrier, reducing conductive heat transfer.Reduction of Heat Gain:
Reflection significantly reduces heat gain from external sources, especially in warm climates.Decrease in Heat Transfer:
The reflection of radiant energy and the thermal break reduce heat transfer to the other side of the material.Additional Insulation Layers:
Reflective materials often work with other types of insulation to further resist conductive and convective heat flows.Regulation of Internal Temperatures:
The final step is stabilizing internal temperatures, keeping spaces cooler in summer and warmer in winter.
Reflective insulation materials use highly reflective surfaces and air spaces to reduce heat transfer, enhancing energy efficiency and comfort.
Importance of Reflectivity in Heat Management
Reflectivity is crucial for effective heat management, with applications in various industries. Let’s explore examples and their technical parameters.
1. Construction Industry
In construction, heat reflecting material helps maintain comfortable indoor temperatures and improve energy efficiency. When used on roofs, they reflect much of the sun’s heat away from buildings, reducing heat absorption.
High-quality reflective materials can achieve reflectivity values over 90%, with aluminum foil-based materials reflecting up to 97% of heat.
2. Automotive Sector
In the automotive industry, reflective materials are used in car interiors to protect occupants from high temperatures, especially in hot climates.
Heat reflecting material typically has reflectivity values of 85% to 90%, effectively rejecting heat and keeping interiors cooler.
3. Aerospace and Aviation
Aerospace engineers use reflective materials to protect aircraft from extreme temperatures during flight. Reflective coatings on the exterior reflect solar heat, preventing overheating.
These coatings usually achieve reflectivity values between 90% and 95%, ensuring effective heat rejection.
4. Energy-Efficient Architecture
In energy-efficient architecture, reflective materials are vital for creating sustainable structures. Windows coated with reflective films allow light in while reflecting heat.
Reflective window films can have reflectivity values up to 80%, minimizing heat gain while providing natural light.
5. Industrial Heat Management
Industries with high-temperature processes, like metallurgy and manufacturing, benefit from reflective materials to control heat transfer and protect equipment.
These materials often exhibit reflectivity values over 90%, ensuring efficient heat management in demanding environments.
Reflectivity plays a critical role in heat management across industries. Reflective materials, with their high reflectance capabilities, contribute to energy efficiency, cost savings, and improved living and working environments.
Why Heat Reflective Materials Matter

Optimizing Thermal Dynamics with Reflective Materials
In an era focused on energy efficiency, reflective materials are crucial for managing thermal dynamics in structures and systems. Thermal insulating materials minimize heat absorption, maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures and reducing the need for air conditioning. This efficiency lowers energy consumption and costs, making them essential in both residential and commercial settings.
Technical Parameters of Reflective Materials
The effectiveness of heat reflecting material is evident in their technical parameters. High-quality materials can reflect up to 97% of radiant heat, significantly reducing indoor temperatures by as much as 30 degrees Fahrenheit. This efficiency cuts down on air conditioning needs and lowers electricity bills.
The Benefits of Using Heat Reflective Materials

Reflective materials play a vital role in modern construction, energy management, and daily living, offering a range of benefits that enhance comfort, efficiency, and sustainability. These materials are specifically designed to reflect heat, helping to keep indoor spaces cooler during summer, reducing the strain on cooling systems, and leading to significant energy savings and lower carbon emissions. In addition to thermal reflection, they selectively reflect visible light while blocking harmful UV rays, ensuring spaces remain well-lit without excessive heat gain. High-quality radiant barriers, for instance, can reflect up to 95% of incoming radiant heat, making them indispensable tools for maintaining energy-efficient environments.
Beyond comfort and efficiency, reflective materials also help protect structures and assets, extending their longevity. For example, in automotive applications, aluminum foil composites act as effective heat shields, safeguarding vehicle interiors from heat damage. Similarly, in construction, these materials reduce heat transfer, providing a durable and efficient solution for insulation.
At WT, we are dedicated to delivering advanced reflective materials tailored to diverse applications. Our product range includes high-performance options, such as aluminum foil composite phenolic boards, which reflect up to 97% of heat while offering impressive durability. The science behind their effectiveness lies in their low-emissivity surfaces, which minimize infrared heat radiation and make them exceptional radiant barriers. With a commitment to excellence, WT continues to innovate and provide solutions that enhance energy efficiency, protect assets, and contribute to comfortable living and working spaces.
What Are Some Reflective Materials That Keep Heat Out?
Usually, reflective materials are divided into two categories: flexible materials (heat reflective fabric material) and plates.
Because of their high cladding ability, heat reflective fabrics are widely used as radiant heat reflective layers for irregular surfaces, such as heat insulation jackets, industrial protective clothing, etc.; heat reflective sheets are usually used for applications requiring high strength. Used in frame structures, such as duct panels, exterior wall insulation panels, etc.
Next, we will show you common heat reflective materials and their respective advantages and disadvantages from two parts: heat reflective fabrics and heat reflective sheets.
Learn More About: What Are Some Heat Proof Materials?
Heat Reflective Fabrics Overview
| Material Name | Characteristics | Performance Parameters | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Aluminized Fiberglass Fabric | Fiberglass base coated with aluminum. Flame-resistant and thermal-reflective. | Reflects up to 95% of radiant heat; resists up to 550°C continuously; emissivity of 0.03. |
| 2 | Silica Fabrics with Reflective Coatings | High-silica yarns with reflective coating. High melting temperature. | Withstands continuous temperatures of 1000°C; high tensile strength; thermal radiation reflectivity varies by coating. |
| 3 | Metalized Polyimide Films | Polyimide films with a metal layer, often aluminum. Chemical and heat resistant. | Reflectivity above 90%; temperature range from -269°C to +400°C; UV resistant. |
| 4 | Metal-Coated Polymer Fabrics (e.g., Mylar) | Polyester film with aluminum. Flexible and moisture-resistant. | Reflects about 97% of radiant heat; temperature range from -70°C to 150°C; low vapor transmission. |
| 5 | E-Glass or S-Glass with Reflective Coatings | Glass fibers coated with reflective materials. Strong and heat-resistant. | E-Glass withstands up to 600°C; S-Glass up to 1000°C; IR reflectivity enhanced by coating. |
| 6 | Gold-Coated Polyimide Films | Polyimide with gold coating. Exceptional reflectivity and corrosion resistance. | Nearly 99% IR reflectivity; wide operational temperature range; emissivity around 0.02 to 0.03. |
| 7 | Outlast® Adaptive Comfort® Materials | Contains PCMs for temperature regulation. Absorb and release heat. | Manages heat through phase change around 28°C to 32°C; not traditionally reflective. |
| 8 | Ceramic Coatings on Textiles | Textiles with ceramic compounds. Thermal protection and stability. | Extreme temperature resistance >1000°C; high IR reflectivity depends on ceramic type; low conductivity. |
Heat Reflective Sheet Overview
| Material Name | Characteristics | Performance Parameters | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Heat Reflective Phenolic Board | Consists of a phenolic foam core with aluminum foil facing on one or both sides. Lightweight and has good thermal insulation properties. Fire-resistant. | Thermal conductivity typically ranges from 0.02 to 0.04 W/(m·K). Fire-resistant with a high fire rating. |
| 2 | Heat Reflective MGO Board | Made from magnesium oxide (MGO), which is fireproof, molded with layers of aluminum foil. Known for its strength, durability, and resistance to mold and mildew. | Thermal conductivity is usually around 0.044 W/(m·K). Highly fire-resistant with excellent structural strength. |
| 3 | Reflective Insulation Foam Board | Foam insulation boards (such as polystyrene, polyurethane, or polyisocyanurate) laminated with aluminum foil. Offers high thermal resistance and reflects radiant heat. | Varies depending on foam type but generally has an R-value of around 5 to 10 per inch of thickness. |
| 4 | Aluminum Foil Laminated Fiberglass Board | Fiberglass insulation board with an aluminum foil laminate. Provides excellent thermal and acoustic insulation. Resistant to moisture and vapor. | Thermal conductivity is typically around 0.032 to 0.042 W/(m·K). Highly effective sound absorber. |
| 5 | Radiant Barrier Sheathing | Structural sheathing panels (like OSB or plywood) coated with aluminum foil to reflect radiant heat. Used in roofing and wall systems. | Reflects up to 97% of radiant heat; R-value addition is minimal but reduces attic temperatures significantly. |
| 6 | Double Reflective Insulation with Bubble Film | Consists of two external layers of aluminum foil reflecting heat, with one or two bubble film layers in between to reduce thermal conduction. | Reflects up to 94% of radiant heat; R-values can range from 1.1 to 6 depending on the bubble layers and air space used. |
| 7 | Aluminum Foil Laminated Mineral Wool Board | Mineral wool board faced with aluminum foil to increase heat reflection. Good thermal and sound insulation, and fire-resistant. | Thermal conductivity typically ranges from 0.035 to 0.040 W/(m·K); non-combustible with high melting point above 1000°C. |
| 8 | Aluminum Foil Laminated Ceramic Fiber Board | A high-temperature insulation board made from ceramic fibers and reinforced with aluminum foil facing. Excellent for high-temperature applications. | Low thermal conductivity around 0.09 to 0.16 W/(m·K); can withstand temperatures up to 1260°C. |
What Is The Most Reflective Material?

Silver (Polished)
- Reflectivity: ~95–99% (visible light).
- Thermal Properties: Reflects visible and thermal radiation efficiently but is sensitive to tarnishing.
Polished silver is considered the most reflective material for visible light, making it ideal for high-precision applications such as scientific instruments, telescopes, and lasers. Due to its exceptional high reflectivity, silver can also serve as a radiant barrier in specialized applications. However, its tendency to tarnish requires protective coatings or maintenance, especially in environments with high humidity or pollutants.

Aluminum (Polished)
- Reflectivity: ~90–95% (visible and infrared light).
- Thermal Properties: Effectively reflects both visible and thermal radiation while being lightweight and corrosion-resistant.
Polished aluminum is a versatile heat reflective material widely used for its combination of high reflectivity, affordability, and durability. Its lightweight nature and heat barrier properties make it ideal for applications like solar panels, lighting reflectors, and spacecraft components. Unlike silver, aluminum is less prone to tarnishing and easier to handle, though its reflective properties are slightly lower. Aluminum foil, in particular, is a common and cost-effective fabric heat reflective material used in both industrial and household settings.

Gold (Polished)
- Reflectivity: ~98% (infrared light), ~90% (visible light).
- Thermal Properties: Gold reflects infrared radiation exceptionally well and remains stable in harsh environments.
Gold’s unique ability to resist tarnishing and corrosion makes it a premium heat reflective material for demanding applications. It is often used in spacecraft, satellites, and radiant heat reflectors, as it can effectively protect equipment from intense solar radiation. Its ability to reflect infrared heat with unmatched efficiency ensures the longevity and performance of sensitive components in extreme conditions. Although expensive, gold is invaluable in high-stakes applications requiring both stability and durability.

White Paints (High-Albedo Coatings)
- Reflectivity: ~85–95% (depends on formulation).
- Thermal Properties: Reflects solar radiation effectively, reducing heat absorption in buildings.
High-albedo white paints are an economical and sustainable solution for reducing heat buildup in urban environments. These coatings are considered energy efficient, as they reduce the need for air conditioning by reflecting sunlight and acting as a heat barrier. Commonly applied to roofs and walls, these paints mitigate urban heat islands and are essential for improving energy efficiency in modern construction. Their heat reflective properties make them especially useful in hot climates, where maintaining indoor comfort is a priority.
Mylar (Metalized Polyester Film)
- Reflectivity: ~90–95% (visible and infrared light).
- Thermal Properties: Retains and reflects thermal radiation effectively, making it an excellent insulator.
Mylar, a highly versatile fabric heat reflective material, is known for its flexibility, durability, and moisture resistance. Its lightweight and high reflectivity make it a preferred choice for emergency blankets to retain body heat and for thermal insulation in sensitive electronic equipment. Mylar is also commonly used in reflective fabric applications due to its consistent heat reflective properties. Its combination of affordability and functionality makes it a reliable choice for both lightweight and industrial applications.

Glass with Reflective Coatings
- Reflectivity: ~85–95% (depends on coating).
- Thermal Properties: Reflective coatings can selectively control heat gain and light transmission.
Glass with reflective coatings is designed to improve energy efficiency in buildings by acting as a radiant barrier, reflecting heat while allowing natural light to pass through. This material is particularly effective in windows, where it reduces cooling costs in hot climates and prevents radiant heat from entering indoor spaces. Reflective glass can also be tailored for aesthetic purposes, serving as both a functional and modern architectural element.
Summary of Applications
- High-precision optics and scientific instruments: Silver, as the most reflective material for visible light.
- Solar panels and cost-effective reflectors: Polished aluminum, including aluminum foil for lightweight solutions.
- Spacecraft and infrared protection: Gold, for its unmatched ability to reflect infrared heat.
- Energy-efficient buildings: High-albedo white paint and reflective glass.
- Emergency insulation and lightweight applications: Mylar, a flexible reflective fabric.
- Fire resistance and structural applications: Magnesium Oxide (MgO), combining high reflectivity and durability.
Case Studies Illustrating the Appropriate Use of Each Material

1. Radiant Barrier Foil Insulation
Ideal for residential attics, radiant barrier foil insulation reflects radiant heat, keeping attics cooler in the summer and warmer in the winter. Case studies have shown significant energy savings in homes with properly installed radiant barriers, reducing the strain on air conditioning and heating systems.
2. Reflective Roofing Membranes
In commercial buildings, reflective roofing membranes have been instrumental in reducing cooling costs. A case study involving a retail store demonstrated a substantial decrease in energy consumption and improved indoor comfort after the installation of a reflective roofing membrane.
3. Aluminum Foil Composite Phenolic Board
Industries with high-temperature processes, such as manufacturing and aerospace, benefit from the use of aluminum foil composite phenolic boards. These boards act as effective heat shields, preventing damage to machinery and ensuring operational safety.
How Effective Radiant Barriers Are in Various Settings
Reflective materials play a vital role in modern construction, energy management, and daily living, offering a range of benefits that enhance comfort, efficiency, and sustainability. These materials are specifically designed to reflect heat, helping to keep indoor spaces cooler during summer, reducing the strain on cooling systems, and leading to significant energy savings and lower carbon emissions. In addition to thermal reflection, they selectively reflect visible light while blocking harmful UV rays, ensuring spaces remain well-lit without excessive heat gain. High-quality radiant barriers, for instance, can reflect up to 95% of incoming radiant heat, making them indispensable tools for maintaining energy-efficient environments.
Beyond comfort and efficiency, reflective materials also help protect structures and assets, extending their longevity. For example, in automotive applications, aluminum foil composites act as effective heat shields, safeguarding vehicle interiors from heat damage. Similarly, in construction, these materials reduce heat transfer, providing a durable and efficient solution for insulation.



