Heat repellent materials are essential in industries facing extreme temperatures and corrosion. These include refractory metals like molybdenum (2,623°C) and tantalum (3,017°C), advanced ceramics such as silicon carbide, and heat-resistant stainless steels.
Refractory metals provide unmatched thermal stability, while ceramics offer superior insulation and protective coatings. Stainless steels, especially austenitic grades like 310 and 316, balance heat and corrosion resistance, making them indispensable in aerospace, power generation, and chemical processing.
Heat repellent materials ensure structural integrity in harsh environments, resisting prolonged exposure to intense heat and corrosion.
what materials reflect heat?
Several materials are known for their ability to reflect heat, which is primarily due to their high reflectivity in the infrared spectrum. Here are some of the most effective heat-reflective materials:
- Aluminum Foil: Commonly used in insulation, aluminum foil has a high reflectivity and is effective at reflecting heat.
- Polished Silver: As mentioned earlier, polished silver surfaces have the highest reflectivity, reflecting up to 95% of radiant energy.
- Polished Aluminum: Similar to aluminum foil, polished aluminum surfaces are excellent at reflecting heat.
- Mylar: A polyester film coated with a thin layer of metal, typically aluminum. It is lightweight and has a high reflectivity.
- Certain White Paints: Some specially formulated white paints have high reflectivity and are designed to reflect solar radiation, reducing heat absorption.
- Aerogels: While not as reflective as metals, silica aerogels are excellent insulators due to their low density and high porosity, which can effectively reduce heat transfer.
- Reflective Fabrics: Fabrics coated with reflective materials or woven with reflective threads can reflect heat, often used in protective clothing.
- Low-E (Low Emissivity) Glass: Coated with a thin, transparent layer of metal, this type of glass reflects infrared radiation while allowing visible light to pass through, reducing heat transfer.
These materials are used in various applications, from building insulation and solar reflectors to personal protective equipment and space technology, where minimizing heat absorption is crucial.
What Is The Most Heat Resistant Material?
Refractory Metals: True Heat Resistance
Venture into the realm of materials, and you’ll find refractory metals holding the fort. These champions, known for their high melting points, are a testament to true heat proof and temperature resilience. They don’t just withstand high temperatures with ease; they maintain their tensile strength and mechanical properties even when the degree Celsius soars.
Corrosion Resistance Warriors
But it’s not all about braving the high heat. These metals are also corrosion resistance warriors, maintaining their integrity even at room temperature where other materials might succumb to the elements. In the universe of materials, refractory metals stand out as the super-strong, high-performance defenders against both extreme heat and corrosion.
Learn More:《What Are Some Heat Proof Materials》
What is the most heat resistant textile?
Aramid Fibers: Unmatched Heat Resistance
Imagine a world of scorching heat, where every degree Celsius matters. Amidst this, one textile stands tall: Aramid fibers. Known for their unmatched heat resistance and impressive melting point, these fibers remain steadfast against extreme temperatures. Even at room temperature, their mechanical prowess is evident. Beyond just battling high heat, Aramid fibers are also corrosion-resistant, showcasing their high performance in diverse conditions. In the realm of textiles, Aramid wears the crown for resilience and heat defense.
Aramid Fibers: Nomex and Kevlar
Aramid fibers, like Nomex and Kevlar, are among the most heat-resistant textiles. They maintain their strength and integrity even when exposed to flames and do not melt, which is why they are commonly used in firefighter suits and other protective clothing.
What type of heat-resistant materials do space vehicles use?
heat resistant material
Space vehicles endure extreme conditions, from fiery re-entries to the cold vacuum of space. Refractory metals, with their high melting points, lead the defense against extreme heat. Ceramic tiles dissipate high temperatures on the spacecraft’s surface, while corrosion-resistant Carbon-Carbon composites protect leading edges during high-speed travel. Together, these materials ensure space vehicles’ safe journeys through the cosmos.
Refractory Metals
Space vehicles use refractory metals like tungsten and molybdenum, which can withstand the high temperatures of re-entry.
Ceramic Tiles
Ceramic tiles, used on the Space Shuttle, dissipate heat and protect the spacecraft from high temperatures.
Carbon-Carbon Composites
Carbon-Carbon composites are used for nose tips and leading edges due to their high thermal resistance.

How heat resistant is silicone?
Silicone: A Versatile Heat-Resistant Material
Silicone can typically withstand temperatures up to 200-250°C (392-482°F) in its standard form. However, specialized silicones can resist even higher temperatures. It’s a popular material for kitchenware, seals, and gaskets because of its heat resistance and non-toxicity.
Flexibility Without Compromise
Silicone stands out in the realm of heat-resistant materials, offering a flexibility that doesn’t compromise on temperature resistance. It confidently faces high temperatures, maintaining its integrity where other flexible materials might waver. Its resilience is evident not just in high temperatures but also at room temperature, presenting steadfast mechanical properties.
Corrosion Resistance and Enduring Performance
Beyond its heat resistance, silicone is notable for its corrosion resistance, enduring various environments with ease. In essence, silicone represents a harmonious blend of flexibility, heat resilience, and enduring performance.
What's the best lightweight, heat-insulating material?
When it comes to balancing lightweight and heat insulation, Aerogel stands unmatched. Often referred to as “frozen smoke“, it defies extreme heat while maintaining feathery lightness. Its impressive temperature resistance means it can withstand high temperatures without issue. Even at room temperature, its tensile strength and resistance to creep are commendable. In the world of heat-resistant materials, Aerogel confidently claims its spot as the go-to lightweight insulator.
What is the cheapest material for thermal insulation?
Cellulose Insulation: Budget-Friendly Thermal Champion
When budget meets the need for effective thermal insulation, cellulose insulation takes center stage. Derived from recycled paper, it’s both wallet and environment-friendly. Despite its affordability, it offers commendable heat resistance, proving its mettle against high temperatures. In the realm of insulation, cellulose stands out as a cost-effective champion, delivering reliable performance without breaking the bank.
Fiberglass: A Common Insulation Choice
Fiberglass is often used in building insulation. It’s relatively cheap, widely available, and offers good thermal insulation properties. However, care needs to be taken during installation due to its irritant nature.
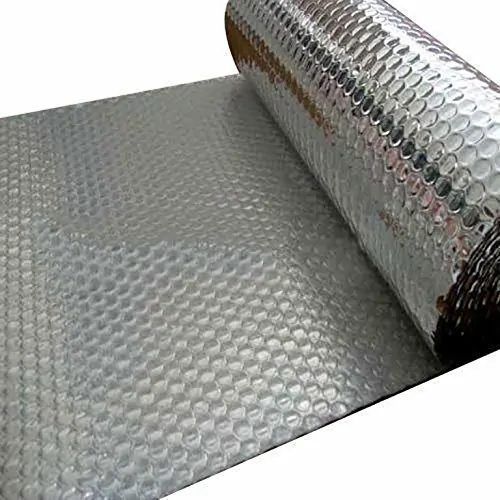

What are some reflective materials that keep heat out?
Dive with me into the universe of reflective materials that combat high temperatures with a simple strategy: reflection.
First on our list is Mylar. These thin films, often seen in emergency blankets, use their reflective properties to send high heat packing. Whether the sun’s blazing at its highest degree Celsius or it’s just a warmer room temperature day, Mylar remains steadfast, reflecting extreme heat away.
Next, we have aluminum foil. A household staple, but did you know it’s also a high-performance heat reflector? Its shiny surface acts like a mirror, turning away temperature surges and ensuring what’s underneath remains cool.
Lastly, reflective paints. These aren’t your ordinary paints. Infused with heat-resistant properties, they offer double-duty protection by reflecting sunlight while providing temperature resistance.
In a world where the fight against high temperature is real, these reflective materials stand tall, offering effective solutions against the onslaught of extreme heat. Simple, yet powerful; they are the unsung heroes in the battle against heat.
What are the materials used in fire retardant clothes?
In the world of fire-retardant fabrics, Nomex stands out with its impressive melting point, offering exceptional protection against high temperatures. And then there’s Kevlar, renowned for its tensile strength and resistance to creep, providing a durable shield against both high heat and corrosion. Proban, a modified cotton fabric, ensures breathability along with reliable heat resistance at varying degrees Celsius. These materials, known for their high-performance characteristics, serve as the unseen guardians in fire-resistant clothing, ensuring safety in extreme conditions.
Aramid Fibers: Fibers like Nomex and Kevlar are widely used.
Nomex: At the heart of fire-resistant clothing lies Nomex, an aramid fiber with an exceptional pedigree. It boasts inherent flame resistance, meaning it doesn’t rely on chemical treatments for protection. Its high melting point and robust mechanical properties make it a go-to choice in environments where safety cannot be compromised.
Kevlar: Known for its extraordinary strength, Kevlar finds its place in protective gear where high tensile strength and temperature resistance are prerequisites. It’s a prime contender in the world of firefighting equipment.
Proban-Treated Cotton: This is cotton treated with a special chemical to make it flame-retardant.
Which insulating materials are used in heat resistant cable?
In our ever-evolving technological world, heat-resistant cables serve as silent workhorses, ensuring that devices run smoothly even when faced with the challenge of extreme heat. The secret? Their insulating materials, designed for optimal heat and temperature resistance.
- PTFE (Teflon): Boasting a high melting point and exceptional heat resistance, PTFE remains stable even at temperatures beyond typical room temperature, reaching degrees Celsius that would challenge lesser materials.
- Silicone Rubber: Valued for its flexibility and heat-resistant properties, it’s especially adept at handling high heat without compromising its mechanical properties.
- Mica: A mineral known for its impressive heat resistance and a melting point among the highest of insulating materials. Mica’s natural properties make it both temperature-resistant and corrosion-resistant, ensuring longevity even in demanding environments.
Are heat resistant materials also fire resistant?
Many heat resistant materials are also fire resistant, meaning they can prevent the spread of fire or resist combustion. However, the terms are not interchangeable, and the specific fire resistance of a material should be evaluated based on its fire rating and performance in fire tests.
How do I maintain heat resistant materials?
Maintenance often involves regular inspections for signs of wear or damage, cleaning to remove any debris or contaminants, and, in some cases, applying protective coatings to extend the material’s lifespan.



